Brain functional connectivity (FC) is often assessed from fMRI data using seedbased methods, such as those of detecting temporal correlation between a predefined region (seed) and all other regions in the brain; In investigations of the brain's resting state using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), a seedbased approach is commonly used to identify brain regions that are functionally connected The seed is typically identified based on anatomical landmarks, coordinates, or the location of brain activity during a separate task To better understand intrinsic brain connections in major depression, we used a neuroimaging technique that measures resting state functional connectivity using functional MRI (fMRI) Three different brain networks—the cognitive control network, default mode network, and affective network—were investigated Compared with controls, in depressed subjects each of
Predicting Functional Networks From Region Connectivity Profiles In Task Based Versus Resting State Fmri Data
Seed region fmri
Seed region fmri-The seed region will be the Posterior Cingulate Gyrus You will identify the seed region using the HarvardOxford Cortical Atlas To start FSL, type the following in the terminal fsl & NB The & symbol allows you to type commands in this same terminal, instead of having to open a second terminal Click FSLeyes to open the viewer Resting state fMRI analysis using seed based and ICA methods Abstract In this paper, we analyze the functional connectivity between the various parts of the brain using resting state fMRI(Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
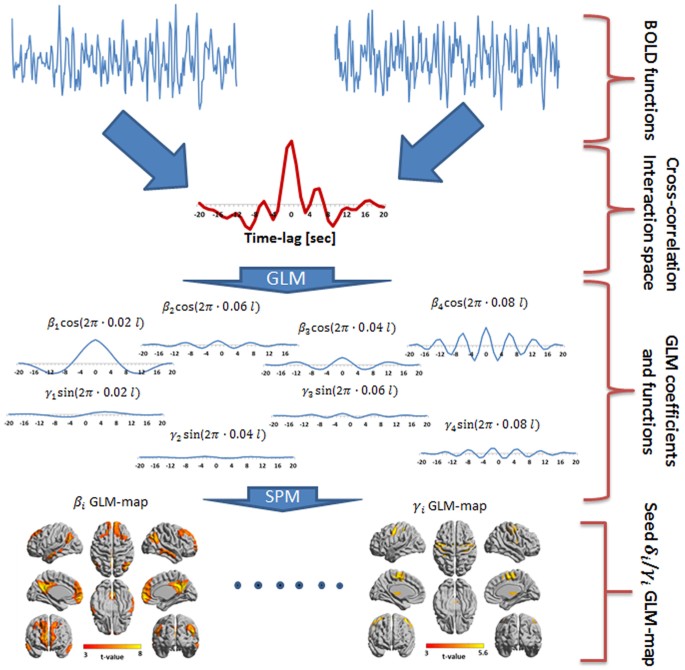



Frequency Phase Analysis Of Resting State Functional Mri Scientific Reports
RestingState fMRI rsfMRI is a method aimed at examining intrinsic networks in the brain while no task is performed (rest);The method of seedbased functional connectivity studies regions correlated with the activity in a seed region In seedbased analysis, the crosscorrelation is identified between the timeseries of the seed and the rest of the brain 9 Zang et al found that the activation of bilateral cerebellum was decreased in ADHD group 10 Therefore, thisPrior functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies indicate that a core network of brain regions, including the hippocampus, is jointly recruited during episodic memory, episodic simulation, and divergent creative thinking
The Resting State (RS fMRI) model performs a seedbased analysis of restingstate fMRI data The user has to specify a seed region, and the model calculates the Pearson correlation map of the seed region signal with the signals of all brain voxels, as well as a Fisher zscore mapSeed = region of interest) Temporal correlation between the time course of every voxel in the brain and the time course from a seed voxel • hypothesisdriven a priori selection of a voxel, cluster, or atlas • the extracted time series is used as regressors in a GLM analysis • univariate approachDeepDyve is the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at your fingertips
The authors identified a seed region in the left somatosensory cortex on the basis of block design fMRI After determining the correlation between the BOLD time course of the seed region and that of all other areas in the brain, the authors found that the left somatosensory cortex was highly correlated with homologous areas in the contralateral hemisphereThis region of interest is typically called seed A seed can be a priori defined region or it can be selected from a traditional task dependent activation map acquired in a separate fMRI experiment, pinpointing a specific region of interestResting state functional MRI (RfMRI) is a relatively new and powerful method for evaluating regional interactions that occur when a subject is not performing an explicit task Lowfrequency (



Predicting Functional Networks From Region Connectivity Profiles In Task Based Versus Resting State Fmri Data



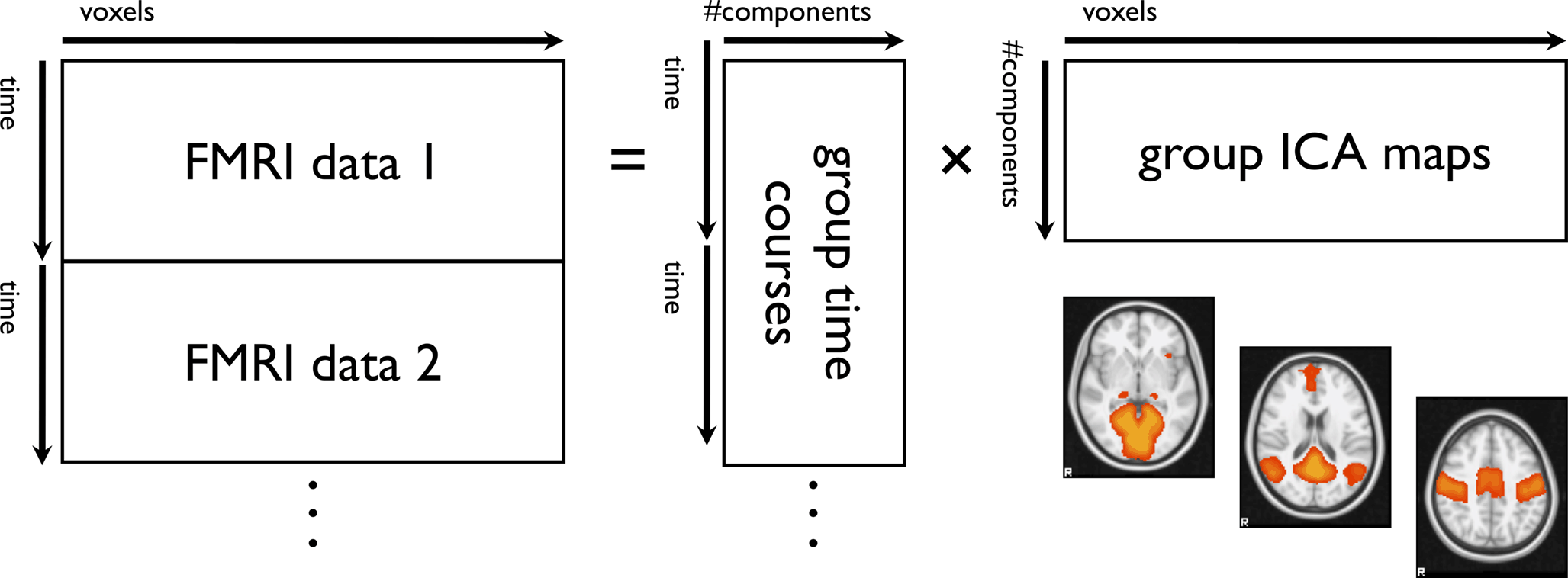
Identifying Resting State Networks From Fmri Data Using Icas By Gili Karni Towards Data Science
Network analysis " Information o Seed region, some or all regions in a networkThis correlation between timeseries of different regions of the brain Restingstate functional connectivity Psychophysiological interaction (PPI) is a brain connectivity analysis method for functional brain imaging data, mainly functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) It estimates contextdependent changes in effective connectivity (coupling) between brain regions Thus, PPI analysis identifies brain regions whose activity depends on an interaction between psychological



The Role Of Resting State Functional Mri For Clinical Preoperative Language Mapping Cancer Imaging Full Text




Fsl Fmri Resting State Seed Based Connectivity Neuroimaging Core 0 1 1 Documentation
Typical FMRI data analysis " Massively univariate (voxelwise) regression y = Xβε " Relatively robust and reliable " May infer regions involved in a task/state, but can't say much about the details of a network !The map represents a restingstate functional connectivity analysis performed on 1,000 human subjects, with the seed placed at the currently selected location Thus, it displays brain regions that are coactivated across the restingstate fMRI time series with the seedMeaningful restingstate fMRI data lies in the frequency range of approximately 001 − 01 Hz By comparison, respiratory fluctuations produce aliased signals in the range of 01 − 03 Hz, while cardiac pulsations produce signals in the range of 08 − 13 Hz Thus physiological noise is a much greater problem for RSfMRI than for task




Resting State Fmri A Review Of Methods And Clinical Applications Abstract Europe Pmc



Frontiers Advances And Pitfalls In The Analysis And Interpretation Of Resting State Fmri Data Frontiers In Systems Neuroscience
Seed = region of interest) • hypothesisdriven a priori selection of a voxel, cluster, or atlas • the extracted time series is used as regressors in a GLM analysis • univariate approach • Advantage • direct answer to aTypical FMRI data analysis " Massively univariate (voxelwise) regression y = Xβε " Relatively robust and reliable " May infer regions involved in a task/state, but can't say much about the details of a network ! restingstate fMRI The brain controls all the complex functions in the human body Structurally, the brain is organized grossly into different regions specialized for processing and relaying neural signals;




Does Resting State Functional Connectivity Differ Between Mild Cognitive Impairment And Early Alzheimer S Dementia Journal Of The Neurological Sciences




Seed Based Connectivity Analysis Of Resting State Fmri Data A Download Scientific Diagram
Or using multivariate methods, such as independent component analysis (ICA) ICA is a useful datadriven tool, but reproducibility issues complicate group inferences based on Restingstate fMRI using the left inferior frontal gyrus as the seed region demonstrated strong correlations with right inferior frontal gyri as well as bilateral Wernicke's area (purple circles) In this case, the conclusion was also aFunctionally, the brain is subspecialized for perceptual and




Figure 3 From A Window Into The Brain Advances In Psychiatric Fmri Semantic Scholar



Ieeexplore Ieee Org Iel7 Pdf
•Seed based correlation analysis (SCA; To apply correlation analysis method for activation detection, one needs to select a seed point time series which is supposed to be activated for this particular brain region in response to the stimulus Then we correlate this fMRI time series from the predefined seed region with the rest of the brain•Seed based correlation analysis (SCA;
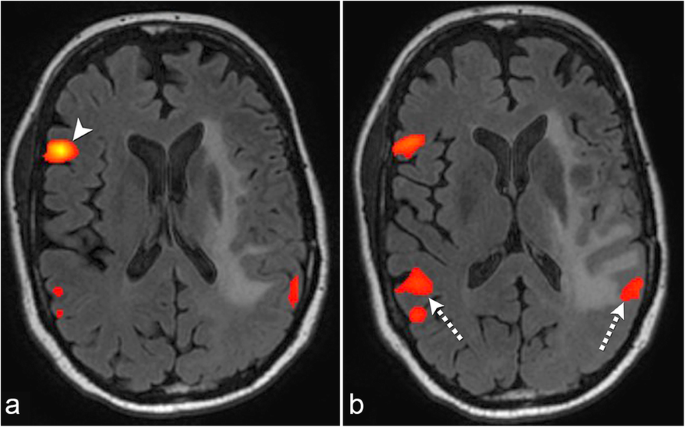



The Role Of Resting State Functional Mri For Clinical Preoperative Language Mapping Cancer Imaging Full Text



Enhanced Regional Functional Connectivity Indicates Seizure Onset Zone Springerlink
We denote the covariates to be a p × 1 vector X ij and the outcome variables to be Y qij where q = 1, ,Q denotes the seed region (Y 1 ij) and its (Q − 1) regions of interest (ROIs), i = 1, , n denotes the ith subject, and j = 1, , J denotes the jth fMRI measurementRecent research into restingstate functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has shown that the brain is very active during rest patterns can be identified based on how similar the time profile is to a seed region's time profile However, this method requires a seed region and can only identify one resting state network at a timeProducing single subject maps of seedtovoxel correlation¶ This example shows how to produce seedtovoxel correlation maps for a single subject based on moviewatching fMRI scans These maps depict the temporal correlation of a seed region with the rest of the brain This example is an advanced one that requires manipulating the data with numpy




Resting State Fmri Wikipedia




Emergence Of Resting State Networks In The Preterm Human Brain Pnas
Electroencephalography (EEG) is the standard diagnosis method for a wide variety of diseases such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, encephalopathies, and coma, among others Restingstate functional magnetic resonance (rsfMRI) is currently a technique used in research in both healthy individuals as well as patients EEG and fMRI are procedures used to obtain direct andFMRI, during which the same subjects performed bilateral finger tapping After determining the correlation between the BOLD time course of the seed region and that of all other areas in the brain, the authors found that the left somatosensory cortex was highly correlated with homologous areas in the contralateral hemisphereThis is to estimate correlations between brain regions These correlations may indicate a tight functional relationship (ie, "functional connectivity") between those regions




Altered Hypothalamic Functional Connectivity In Cluster Headache A Longitudinal Resting State Functional Mri Study Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry



Http Www Gestaltrevision Be Pdfs Lss14 Dm Leuven 12 Aug 14 Pdf
Resting state fMRI analysis using sparse dictionary learning in SPM framework Brain always be active even people are in rest In the resting period, it has been observed that particular groups of brain region are always coactivated These regions are functionally connected each other and each group is called as intrinsic connectivity networkSeedbased connectivity metrics characterize the connectivity patterns with a predefined seed or ROI (Region of Interest) These metrics are often used when researchers are interested in one, or a few, individual regions and would like to analyze in detail the connectivity patterns between these areas and the rest of the brainCalculate group average of Fisher z scores 4Perform two sample ttest of group averages



Www Cell Com Neuron Pdfextended S06 6273 19 3




Common Functional Networks In The Mouse Brain Revealed By Multi Centre Resting State Fmri Analysis Sciencedirect
A voxelwise FC analysis of each ROI was performed for the preprocessed fMRI data For each subject and each seed region (namely ROI), a FC map of the whole brain was obtained by computing the correlation coefficients between the averaged time series of seed region and the time series of the remaining whole brain voxels First, however, we will need to create and place the seed region appropriately We can place a seed voxel in the vmPFC using the XYZ coordinates 0, 50, 5 (similar to MNI coordinates of 0, 50, 5), and a correlation coefficient willRequire a predefined seed region The reconstructed functional network might heavily depend on the sizes and localizations of the seed region s Volumebased data driven methods, such as independent component analysis (ICA) 3, treat the whole brain as a 3D image, usually neglecting the anatomical and biological differ ences between brain



Multimodal Neuroimaging Of Prosody Applied Social Neuroscience And Perception Laboratory




Frequency Phase Analysis Of Resting State Functional Mri Scientific Reports
For each seed location, a sphere of 6mm radius was defined as the seed region and a reference time course was generated by averaging the time courses over the voxels within the region The rsfMRI connectivity map was computed using Pearson correlation between the reference time course and that of each voxel in the brain (voxel size = 375 ×In investigations of the brain's resting state using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), a seedbased approach is commonly used to identify brain regions that are functionally connected The seed is typically identified based on anatomical landmarks, coordinates, or the location of brain activity during a separate task1Identify seed region and regions of interest;



Identifying Resting State Networks From Fmri Data Using Icas By Gili Karni Towards Data Science




Andy S Brain Blog
Dynamics of restingstate functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) provide a new window onto the organizational principles of brain function Using stateoftheart signal with the time course of a preselected seed region, and spatial ICA, which identifies components using a proxy of statistical independence17, have been most widely Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has become a powerful tool to study brain dynamics with relatively fine spatial resolution One popular paradigm, given the indirect nature of the method, is the block design, alternating task blocks with blocks of passive rest Voxels showing a correlation with the seed region above a certainGet a statistical map showing, for each voxel, correlation with seed region This is the core of functional connectivity;



Resting State Functional Mri Everything That Nonexperts Have Always Wanted To Know American Journal Of Neuroradiology



Mriquestions Com Uploads 3 4 5 7 Heuvel Reviewbrainnets1 Pdf
Restingstate fMRI (rsfMRI) has been widely used to segregate the brain into individual modules based on the presence of distinct connectivity patterns Many parcellation methods have been proposed for brain parcellation using rsfMRI, but their results have been somewhat inconsistent, potentially due to various types of noiseSummarize regions by average time course 2For each subject, calculate correlations between seed region and other regions of interest 3Transform Pearson correlations by Fisher's z;Task fMRI Investigators specify a seed voxel or region that they know to be part of a network of interest, from which a characteristic time series is extracted This time series is then used in the same way as a task regressor to identify voxels that share this time course, representing brain areas with connectivity to the seed (ie RSNs) 3




Disrupted Functional Connectivity Of The Periaqueductal Gray In Chronic Low Back Pain Sciencedirect



Med Stanford Edu Content Dam Sm Scsnl Documents Chen Estimation Of Resting State 13 Pdf
Resting state fMRI (rsfMRI or RfMRI) is a method of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) that is used in brain mapping to evaluate regional interactions that occur in a resting or tasknegative state, when an explicit task is not being performed A number of restingstate conditions are identified in the brain, one of which is the default mode network However, using the same rsfMRI data, with the seed region defined in the canonical counterpart of the Broca's area according to the standard coordinates, the seedbased FC mapping (Fig 4E,FNetwork analysis " Information o Seed region, some or all regions in a network




Concepts And Principles Of Clinical Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Chapter 13 The Cambridge Handbook Of Research Methods In Clinical Psychology




A Window Into The Brain Advances In Psychiatric Fmri




Figure 2 From Multi Echo Fmri Resting State Connectivity And High Psychometric Schizotypy Semantic Scholar



Resting State Functional Mri Everything That Nonexperts Have Always Wanted To Know American Journal Of Neuroradiology



Ppt Connectivity Analysis In Afni Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Identifying Resting State Networks From Fmri Data Using Icas By Gili Karni Towards Data Science




Rsfc Correlations Seed Regions Consisted Of The 5 Functional And 2 A Download Scientific Diagram




Defining The Seed Region Of Interest Ppi Analysis Investigates Download Scientific Diagram




An Analytical Workflow For Seed Based Correlation And Independent Component Analysis In Interventional Resting State Fmri Studies Sciencedirect




Localized Prediction Of Glutamate From Whole Brain Functional Connectivity Of The Pregenual Anterior Cingulate Cortex Biorxiv



Plos One Unravelling The Intrinsic Functional Organization Of The Human Striatum A Parcellation And Connectivity Study Based On Resting State Fmri




Fsl Fmri Resting State Seed Based Connectivity Neuroimaging Core 0 1 1 Documentation
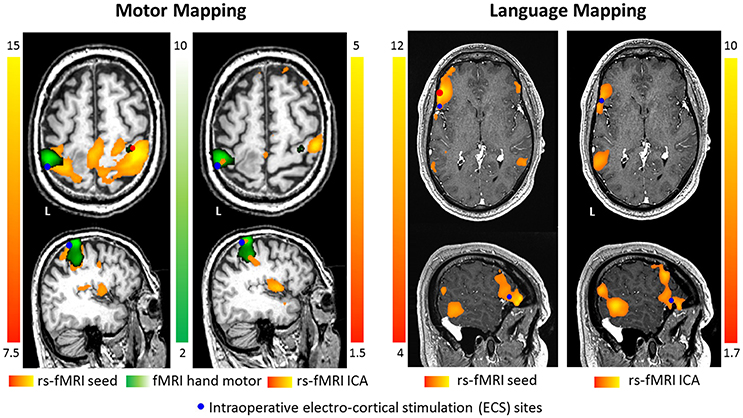



Frontiers Pre Surgical Brain Mapping To Rest Or Not To Rest Neurology




Interaction Between Scene And Object Processing Revealed By Human Fmri And Meg Decoding Journal Of Neuroscience
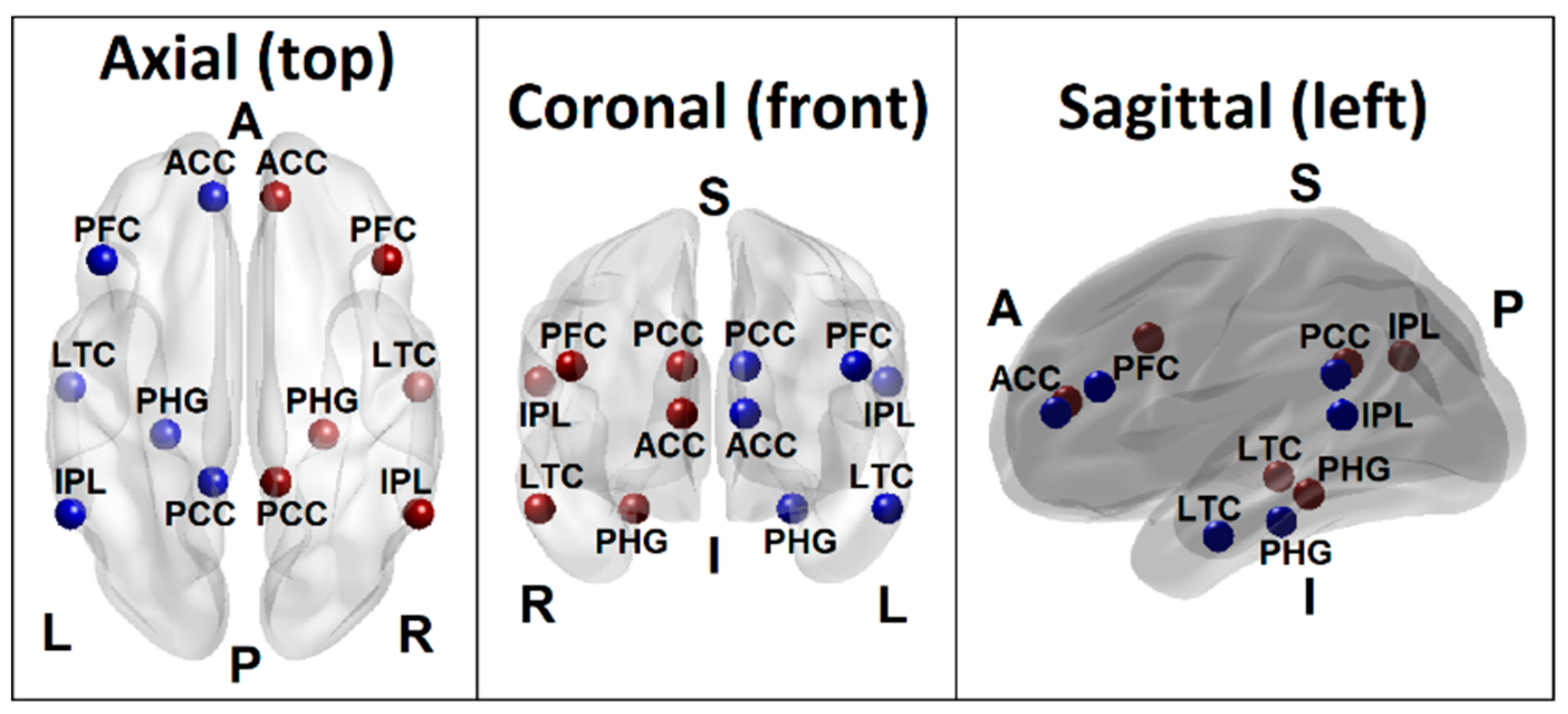



Brain Sciences Free Full Text Random Forest Classification Of Alcohol Use Disorder Using Fmri Functional Connectivity Neuropsychological Functioning And Impulsivity Measures Html
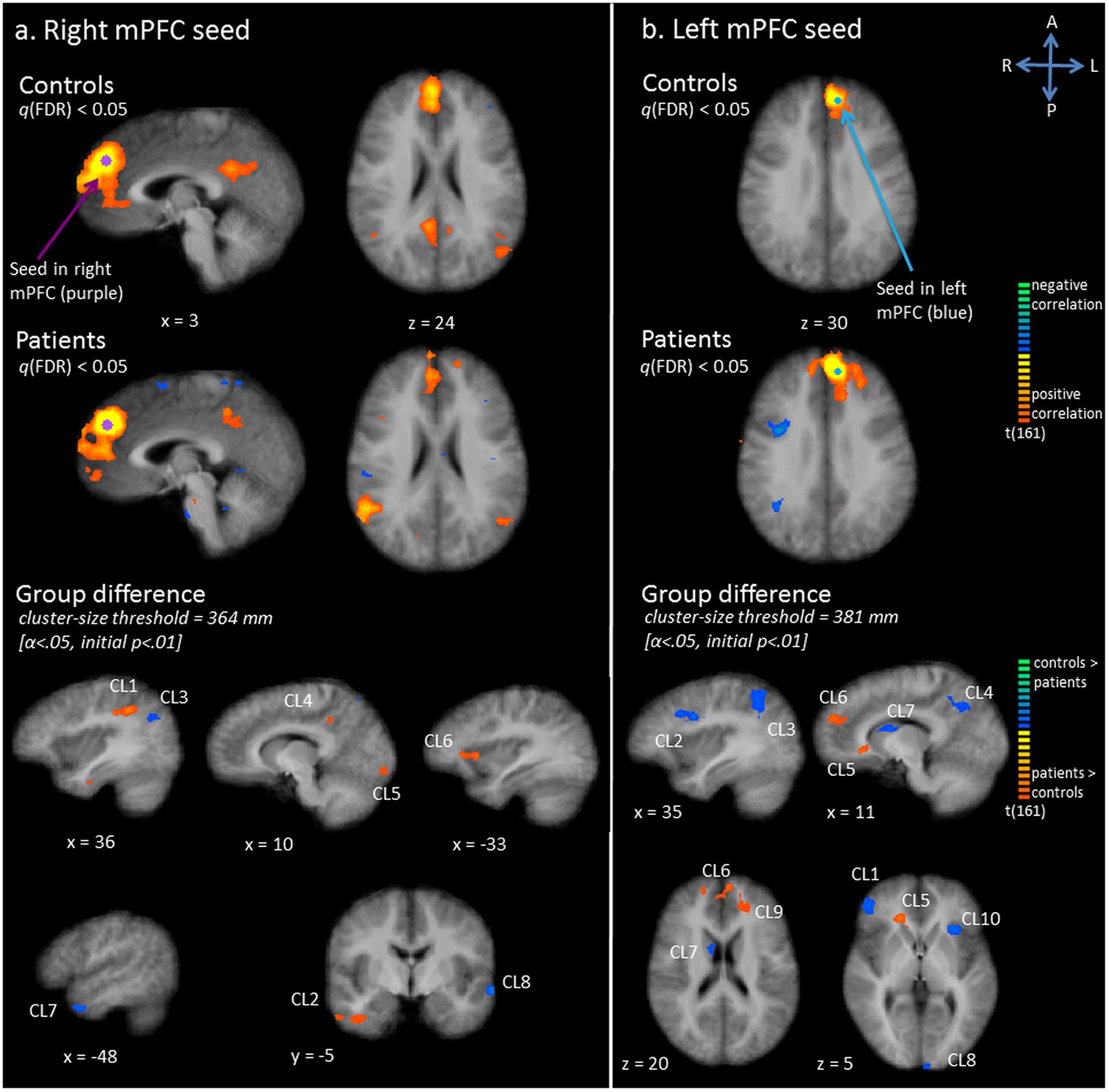



Exploration Of The Brain In Rest Resting State Functional Mri Abnormalities In Patients With Classic Galactosemia Scientific Reports
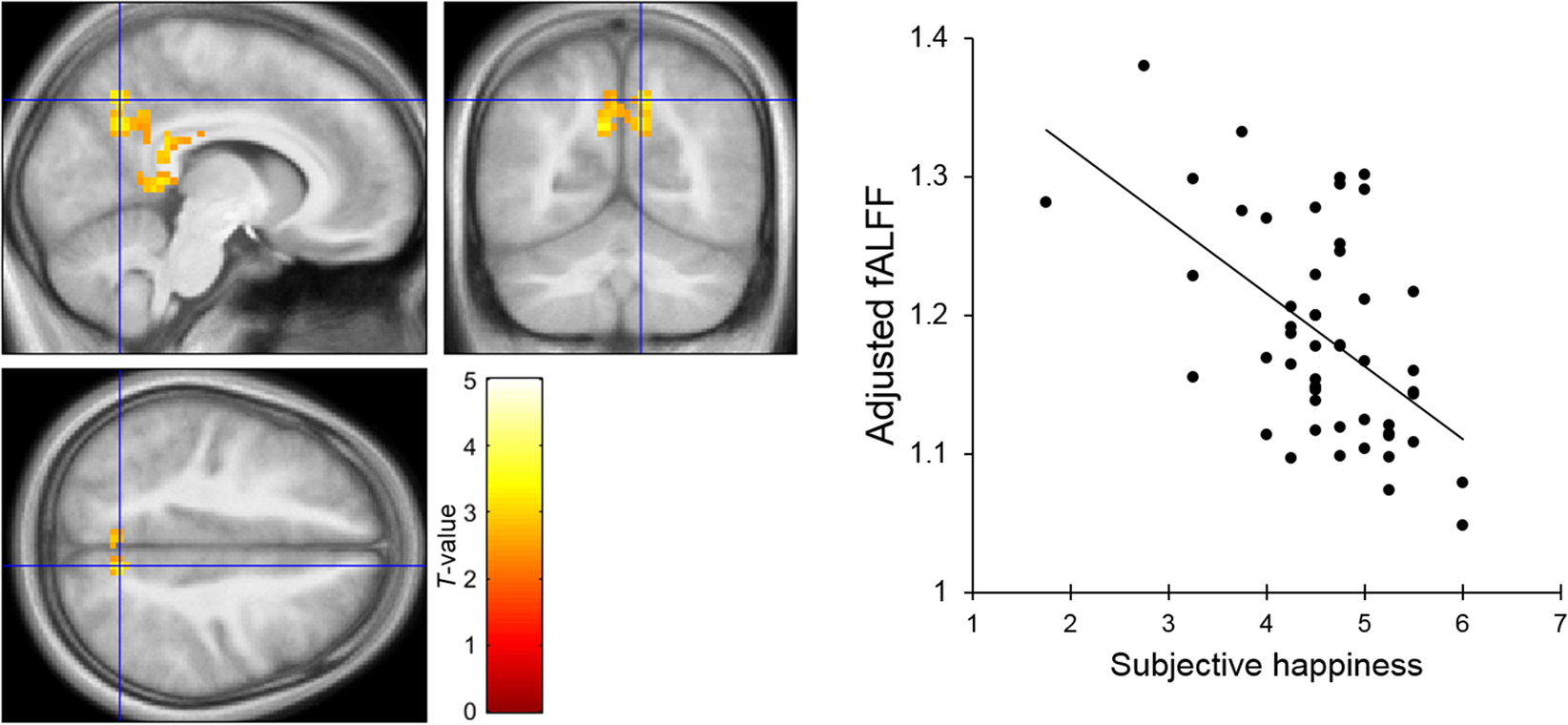



Resting State Neural Activity And Connectivity Associated With Subjective Happiness Scientific Reports
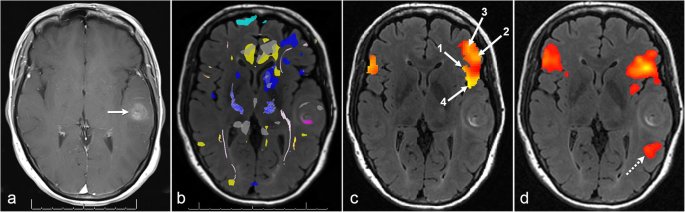



The Role Of Resting State Functional Mri For Clinical Preoperative Language Mapping Cancer Imaging Full Text




A Longitudinal Study Of Changes In Resting State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Functional Connectivity Networks During Healthy Aging Brain Connectivity




Fsl Fmri Resting State Seed Based Connectivity Neuroimaging Core 0 1 1 Documentation




Functional Connectomics From Resting State Fmri Trends In Cognitive Sciences




Defining The Seed Region Of Interest Ppi Analysis Investigates Download Scientific Diagram
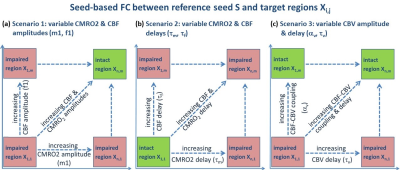



Ismrm Digital Posters Page Fmri Connectivity




Assessing Functional Connectivity In The Human Brain By Fmri Abstract Europe Pmc




There Were Significant Fc Fmri Values Relative To The Pcc Seed Region Download Scientific Diagram




Machine Learning In Resting State Fmri Analysis Sciencedirect



Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 2f978 3 319 567 2 9077 1 Pdf
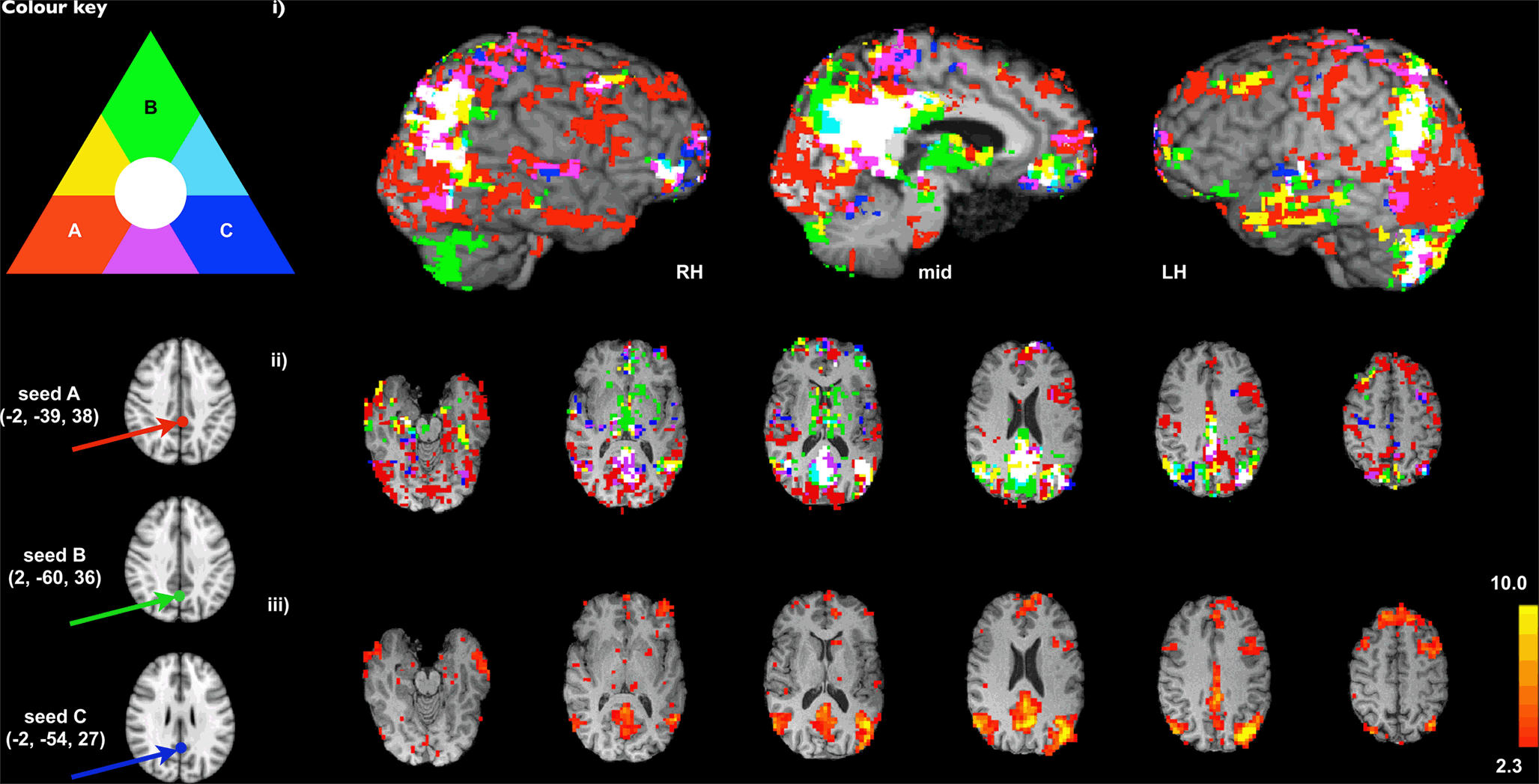



Frontiers Advances And Pitfalls In The Analysis And Interpretation Of Resting State Fmri Data Frontiers In Systems Neuroscience




Resting State Fmri Wikipedia




Maps Of Seed Based Resting State Fmri Functional Connectivities The Download Scientific Diagram



Plos One Coupled Intrinsic Connectivity Distribution Analysis A Method For Exploratory Connectivity Analysis Of Paired Fmri Data



1
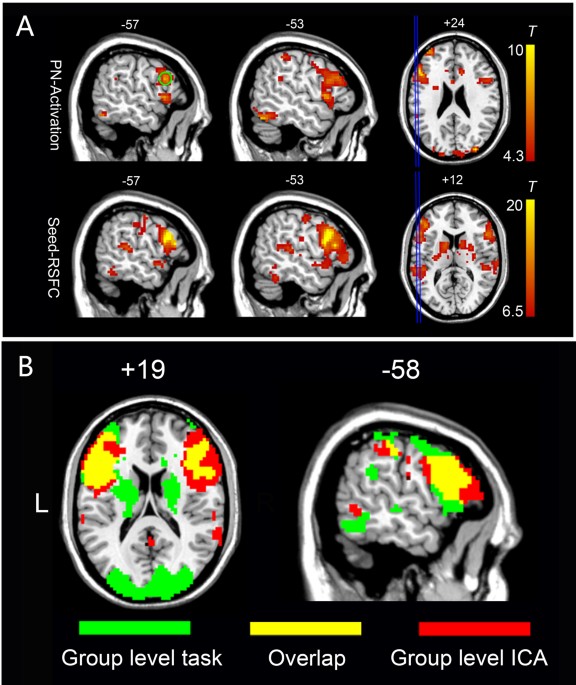



An Automated Method For Identifying An Independent Component Analysis Based Language Related Resting State Network In Brain Tumor Subjects For Surgical Planning Scientific Reports



Plos One Resting State Fmri Reveals Diminished Functional Connectivity In A Mouse Model Of Amyloidosis



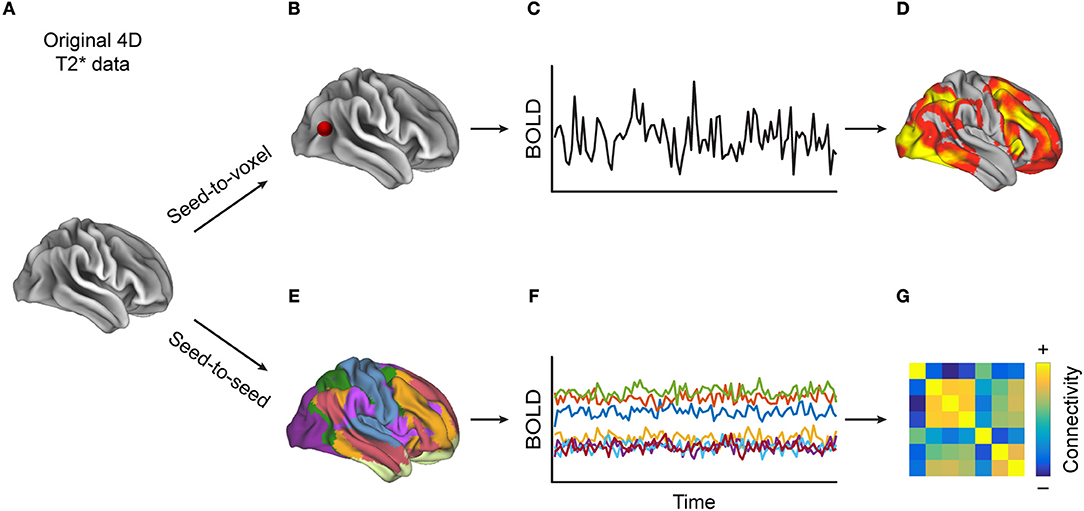
Behavioral Sciences Free Full Text Brain Activations And Functional Connectivity Patterns Associated With Insight Based And Analytical Anagram Solving Html




Machine Learning In Resting State Fmri Analysis Deepai



1



Resting State Functional Mri Everything That Nonexperts Have Always Wanted To Know American Journal Of Neuroradiology




Time Varying Functional Network Information Extracted From Brief Instances Of Spontaneous Brain Activity Pnas



Plos One Resting State Fmri Reveals Diminished Functional Connectivity In A Mouse Model Of Amyloidosis




Seed Roi Used For Functional Connectivity Analyses The 11 Seed Regions Download Scientific Diagram




Language Lateralization From Task Based And Resting State Functional Mri In Patients With Epilepsy Rolinski Human Brain Mapping Wiley Online Library



Resting State Seed Based Analysis An Alternative To Task Based Language Fmri And Its Laterality Index American Journal Of Neuroradiology
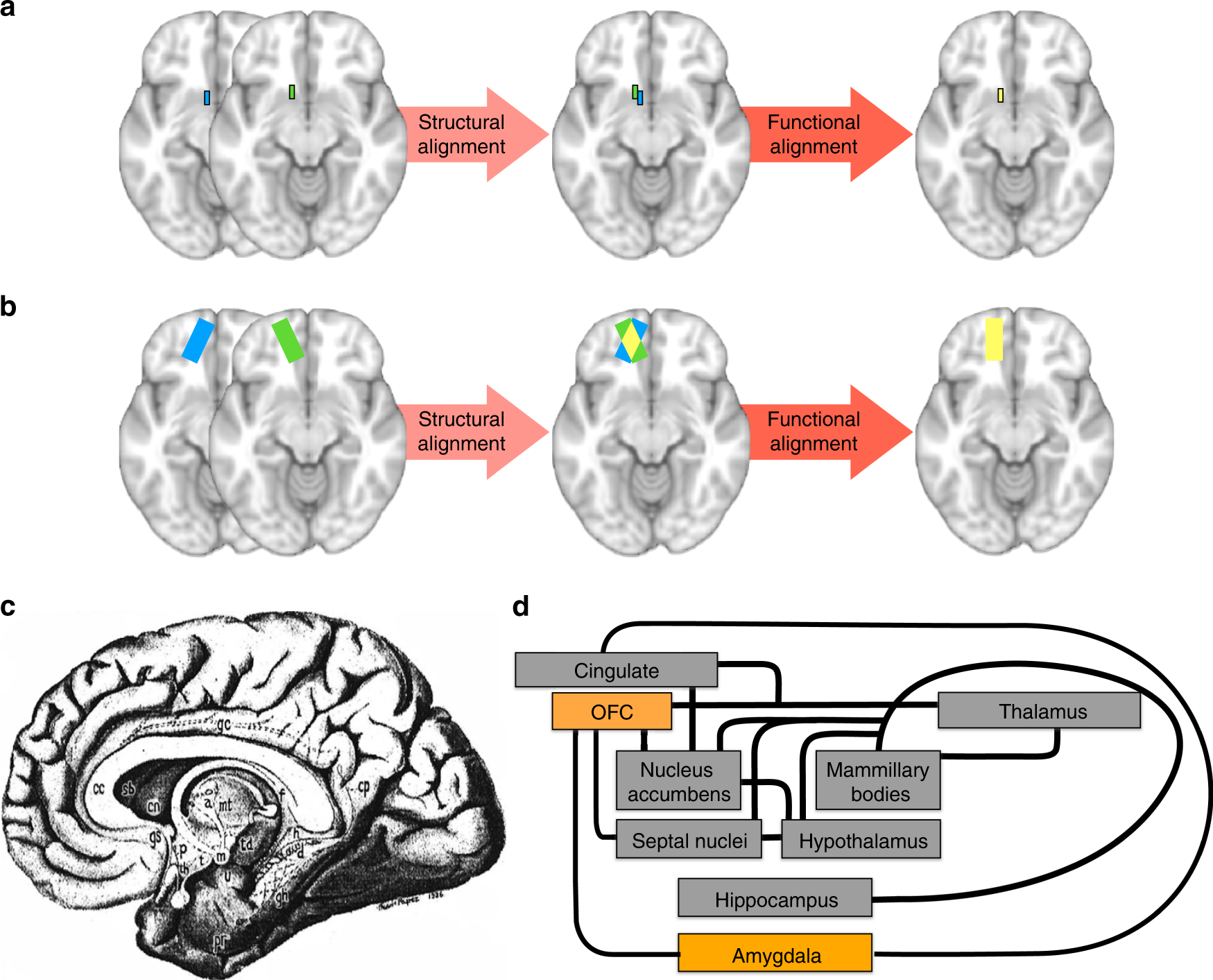



An Improved Neuroanatomical Model Of The Default Mode Network Reconciles Previous Neuroimaging And Neuropathological Findings Communications Biology




Figure 3 From Localization Of Broca S And Wernicke S Areas With Resting State Fmri Semantic Scholar




Seed Based Connectivity Analysis Of Resting State Fmri Data A Download Scientific Diagram



1




Oscillatory Brain States Govern Spontaneous Fmri Network Dynamics Biorxiv




Resting State Fmri Wikipedia




Active And Passive Fmri For Presurgical Mapping Of Motor And Language Cortex Intechopen




Changes In Resting State Functional Brain Activity Are Associated With Waning Cognitive Functions In Hiv Infected Children Abstract Europe Pmc




Mapping Cognitive And Emotional Networks In Neurosurgical Patients Using Resting State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Neurosurgical Focus Volume 48 Issue 2




Seed Based Correlation Analysis Sca And Dual Regression C Pac 1 8 0 Beta Documentation




Seed Based Resting State Fmri Functional Connectivity Matrices




Characterizing The Spectrum Of Task Fmri Connectivity Approaches Ppt Download




High Amplitude Cofluctuations In Cortical Activity Drive Functional Connectivity Pnas




Presurgical Resting State Functional Mri Language Mapping With Seed Selection Guided By Regional Homogeneity Hsu Magnetic Resonance In Medicine Wiley Online Library




Seed Regions Of The Seed Based Resting State Analysis Seed Regions And Download Scientific Diagram




Changes In Thalamus Connectivity In Mild Cognitive Impairment Evidence From Resting State Fmri European Journal Of Radiology




Effects Of Isoflurane Anesthesia On Resting State Fmri Signals And Functional Connectivity Within Primary Somatosensory Cortex Of Monkeys Wu 16 Brain And Behavior Wiley Online Library
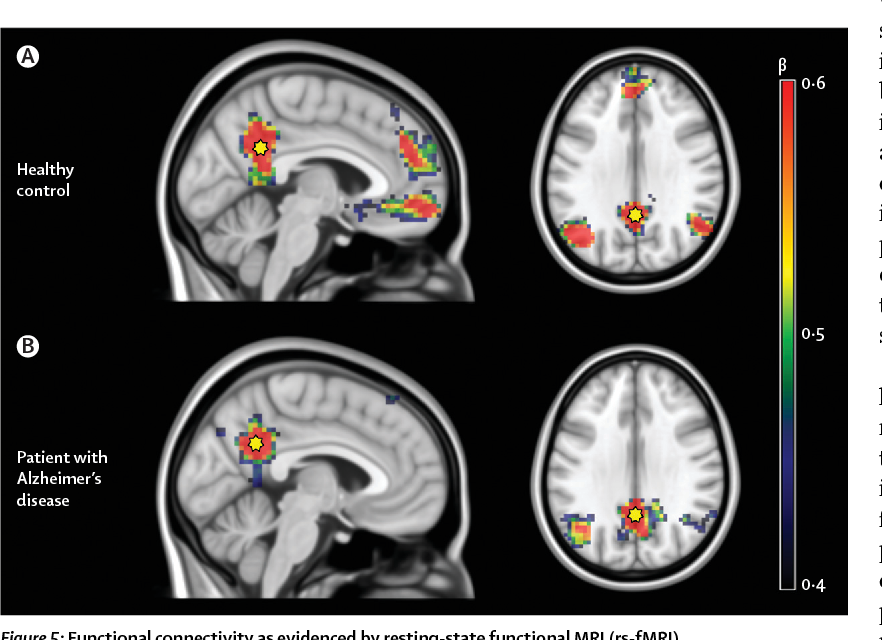



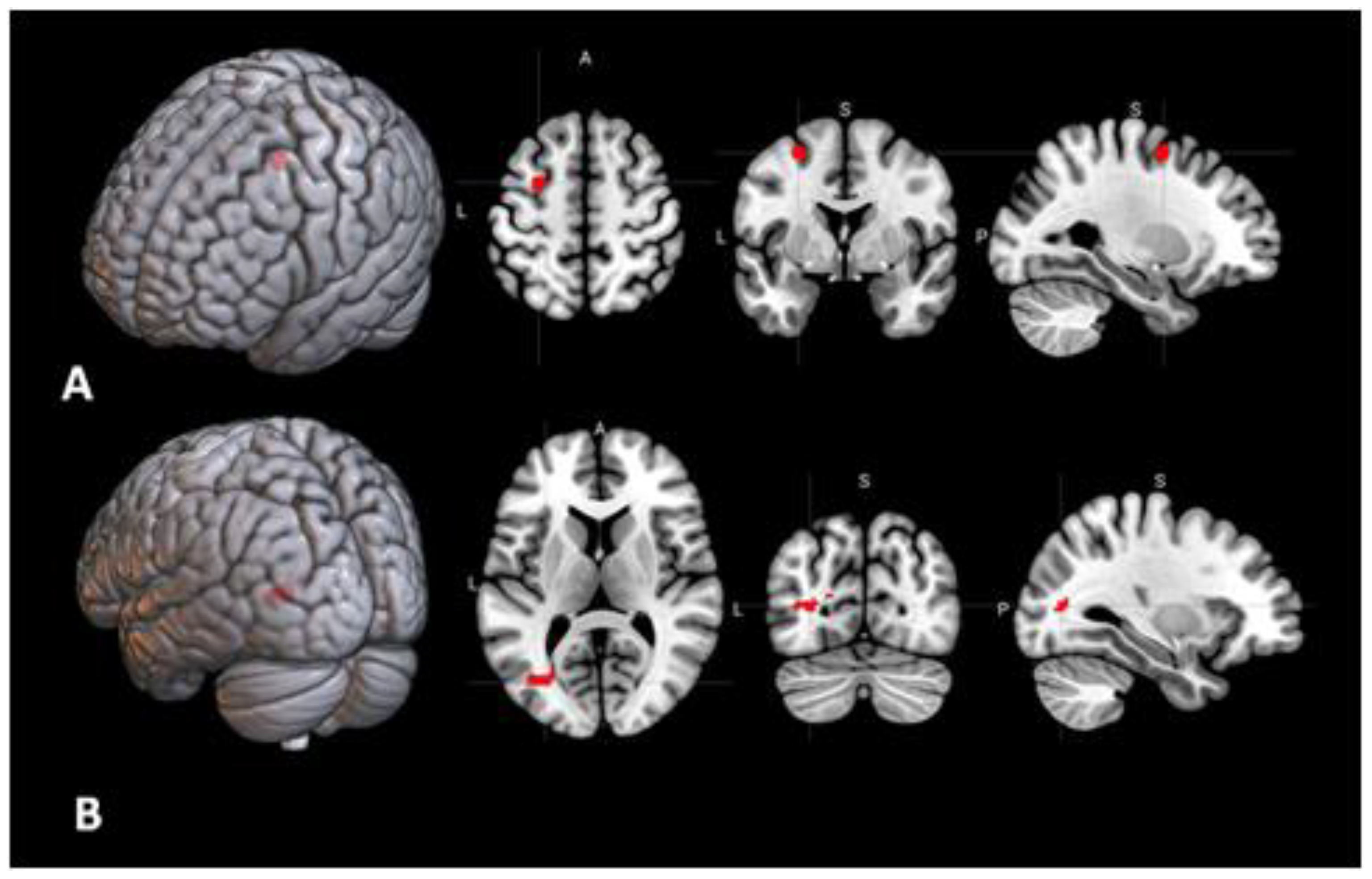
Figure 5 From Multimodal Imaging In Alzheimer S Disease Validity And Usefulness For Early Detection Semantic Scholar



Mriquestions Com Uploads 3 4 5 7 Heuvel Reviewbrainnets1 Pdf




Resting State Fmri Wikipedia




Fsl Fmri Resting State Seed Based Connectivity Neuroimaging Core 0 1 1 Documentation




Fsl Fmri Resting State Seed Based Connectivity Neuroimaging Core 0 1 1 Documentation




Fsl Fmri Resting State Seed Based Connectivity Neuroimaging Core 0 1 1 Documentation



Frontiers Functional Connectivity In Multiple Sclerosis Recent Findings And Future Directions Neurology



1




The Human Brain Is Intrinsically Organized Into Dynamic Anticorrelated Functional Networks Pnas



Www Tnu Ethz Ch Fileadmin User Upload Documents Publications 17 17 Cole Pdf



Seizure Frequency Can Alter Brain Connectivity Evidence From Resting State Fmri American Journal Of Neuroradiology




Active And Passive Fmri For Presurgical Mapping Of Motor And Language Cortex Intechopen




Use Of Resting State Fmri In Planning Epilepsy Surgery



Resting State Functional Mri Everything That Nonexperts Have Always Wanted To Know American Journal Of Neuroradiology




Resting State Fmri An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Human Posterior Insula Functional Connectivity Differs Between Electrical Pain And The Resting State Brain Connectivity



Cancerimagingjournal Biomedcentral Com Track Pdf 10 1186 S 0 W Pdf




A Window Into The Brain Advances In Psychiatric Fmri



No comments:
Post a Comment